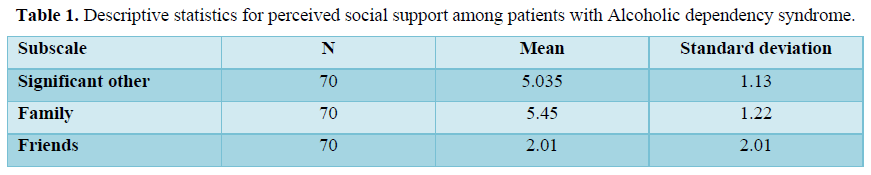INTRODUCTION
Perceived Social support
Social support has been described as “support accessible to an individual through social ties to other individuals, groups, and the larger community.” (Fatih Ozbay) Social support is composed of three components. These are affection, approval and assistance. It is the expression of effect, love and respect. Approval is the appreciation of the suitability of individual attitude and behaviors. Assistance includes direct assistance behaviors like cooperation and lending money.
Social support refers to the provision of psychological and material resources by a social network to help individuals to cope up with their stress. It involves the components of care, empathy and concern for the ones in need. It may range from helping a person in daily tasks, giving advices to helping the ill, providing financial assistance. This is the objective view point of social support.
The subjective view point of the individual who receives this social support describes his perception about the social support which is been received from his surroundings. Perceived social support is individual's cognitive perception that. S/he has established reliable bonds with others and that others provide support to them. (Yamaç, 2009: 68). Provided social support means the behaviors and actions others display.
Social support has been proved to moderate genetic and environmental vulnerabilities for mental illness by facilitating the psychological factors such as fostering the effective coping strategies. The provision of social support
INTRODUCTION
Perceived Social support
Social support has been described as “support accessible to an individual through social ties to other individuals, groups, and the larger community.” (Fatih Ozbay) Social support is composed of three components. These are affection, approval and assistance. It is the expression of effect, love and respect. Approval is the appreciation of the suitability of individual attitude and behaviors. Assistance includes direct assistance behaviors like cooperation and lending money.
Social support refers to the provision of psychological and material resources by a social network to help individuals to cope up with their stress. It involves the components of care, empathy and concern for the ones in need. It may range from helping a person in daily tasks, giving advices to helping the ill, providing financial assistance. This is the objective view point of social support.
The subjective view point of the individual who receives this social support describes his perception about the social support which is been received from his surroundings. Perceived social support is individual's cognitive perception that. S/he has established reliable bonds with others and that others provide support to them. (Yamaç, 2009: 68). Provided social support means the behaviors and actions others display.
Social support has been proved to moderate genetic and environmental vulnerabilities for mental illness by facilitating the psychological factors such as fostering the effective coping strategies. The provision of social support to the psychiatrically ill population is proved to be effective.
Resilience
Resiliency is the ability of a person to recover quickly from a sudden change or misfortune without being overwhelmed, dysfunctional or harmful to oneself as well towards others, and to overcome the difficulties without much strain and raising back to the life again. Some factors that contribute for the person to be resilient are positive attitude, optimism, the ability to regulate one’s emotions, and the ability to see failure as a helpful feedback. It is a real mental work to transcend hardships.
The results of many studies also showed that the resiliency is significantly correlated with the perceived social support in a positive way [1]. The role of perceived social support in promoting the resiliency also found to be prominent along with other factors.
There are many researches which indicates that increased of resiliency is inversely proportional to alcohol misuse and also few other studies indicate that providing the effective lifestyle training to enhance resiliency can also help in relapse prevention for the people with substance abuse [2,3].
Alcohol dependency syndrome: World health organization (WHO) describes it as a state of psychic and usually also physical, resulting from taking alcohol, characterized by behavioral and other responses that always include a compulsion to take alcohol on a continuous or periodic basis in order to experience its psychic effects, and sometimes to avoid the discomfort of its absence; tolerance may or may not be present” [4]. The prevalence of current drinking increased from 45 to 47%. More than 10 million cases were observed with ADS in India.
A problematic usage of alcohol in ADS follows some patterns such as intake of alcohol in a larger quantity for a prolonged period of time, persistent desire for alcohol use, spending a great deal of time in the usage of alcohol and to recover from its effects, a strong desire to use alcohol, recurrent alcohol usage leading to failure to fulfil one’s responsibility at work, school and home, continued use of alcohol despite of experiencing persistent social and interpersonal problems, giving up important social, occupational and recreational activities for the purpose of alcohol, recurrent alcohol use that leads to physical hazards, continuation of alcohol use despite of knowing its effects on one’s physical and psychological health, a need for markedly increased amounts of alcohol to achieve intoxication or desired effect (tolerance), manifestation of withdrawal symptoms; tremors, perspiration, vomiting sensation, cognitive deficits , psychological and behavioral problems - when tried to keep away from it.
The possible causes for alcohol abuse could be failures in parental guidelines, psychological vulnerability, stress, tension reduction and reinforcement, marital and other intimate relationships and expectations of social success.
There are many studies which focuses on the impact of increased perceived social support and resiliency of an individual on the behaviors of substance abuse. Majority of the researches indicates that increased level of perceived social support and resiliency will improve the treatment outcomes and also reduces the extent alcohol abuse.
The de-addiction and the rehabilitation centers are that which mainly focuses on pulling back those addicts from substances; alcohol and to bring back to the normal societal stream by including certain intervention plans to work on their levels of resiliency and motivation to overcome from their addiction. Those activities include group therapy, supportive psychotherapy, occasional training and different activities to introspect more about his abilities and the goals.
The results of the exploratory analysis reveal that specific sources - family and friends and forms (reassurance and worth) of social support are important to the recovering of alcoholic and that the effect of social support on treatment outcome is independent of alcoholic’s history of prior treatment failure. Interventions or program modification programs should be designed specifically to bolster these facets of social support rather than addressing more general forms of support [5].
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A study conducted by Havassy [6] by the name “Social support and relapse: commonalities among alcoholics, opiate users, and cigarette smokers” with a sample size of 221, revealed the importance of social integration and abstinence-specific functional support in predicting the risk of relapse, independent of the particular drug of abuse.
A study conducted by Dobkin [7] by the name “The role of functional social support in treatment retention and outcomes among outpatient adult substance abusers” with a sample size 206, using the questionnaire pertaining to social support, stress and psychological functioning and Addiction severity index. The results of this study revealed that; Higher functional social support at intake is a positive predictor of retention in treatment, and a modest predictor of reductions in alcohol intake.
An exploratory analysis by Beattie [8] by the name “General and alcohol-specific social support following treatment” on private outpatients revealed that social support is the moderator of treatment outcomes and to prevent them from drinking behaviors.
A study by Rosenberg [9] with the title “Relapsed versus non-relapsed alcohol abusers: coping skills, life events and social support” The results of this study indicated that non-relapsers were reportedly less likely to drink and more noncompliant towards problematic situations, and experienced fewer negative life events and more positive life events, than relapsers. The social support results were inconclusive, in this study.
A study by Green [2] with the title “Alcohol misuse and psychological resilience among U.S. Iraq and Afghanistan era veterans” with the sample size of 1090 by using the questionnaires of probable post-traumatic stress disorder, psychological resilience and alcohol misuse. The findings of the study indicated that increased psychological resilience is inversely related to alcohol misuse and is protective against alcohol misuse over time.
A study by Whitbeck [10] with the title “Discrimination, historical loss and enculturation: culturally specific risk and resiliency factors for alcohol abuse among American Indians” on a sample of 452. This study provided a new result - the evidences that historical loss affects and also resiliency effects the enculturation on alcohol abuse among American-Indian alcohol abusers.
A cross-sectional study by Wingo [11] with the title “Resilience characteristics mitigate tendency for harmful alcohol and illicit drug use in adults with a history of childhood abuse: A cross-sectional study of 2024 inner-city men and women”. Associations between resilience and substance use were examined with linear regression models. Their findings suggested that resilience characteristics mitigate risks not only for PTSD, major depression, and suicidality, but also for substance use problems in adults exposed to childhood abuse or other traumatic experiences.
In a semi-experimental study of 26 subjects by the authors Jafari [3] - the subjects were assessed using the Conner-Davidson Resiliency scale. 12 sessions of coping skills training were given to the controlled group, Data were analyzed using t-test and ANCOVA. The obtained results indicated that the life style training was effective in resiliency enhancement and relapse prevention for people with substance dependency.
METHODS
Objectives
- To assess the relationship between perceived social support and resiliency among patients with Alcoholic dependent syndrome.
- To study the role of perceived social support on resiliency among patients with Alcoholic dependent syndrome.
Hypotheses
- There is no significant relationship between perceived social support and resiliency among patients with alcoholic dependency syndrome.
- Perceived social support does not influence resiliency among patients with Alcoholic dependency syndrome.
Sample
Present study was carried out with70 samples diagnosed with Alcoholic dependency syndrome. The samples were selected using purposive sampling method from different rehabilitation center in Shivamogga city.
Inclusion Criteria
- Alcoholic dependency Syndrome patients with other substance use are included.
- Patients with neurological and psychotic problems were also included.
Exclusion Criteria
Alcoholic dependency syndrome patients with physical disabled were excluded.
Dependent Variables
Resiliency.
Independent Variables
Perceived social support.
Research Design
Correlational design.
Tools
The Multi-dimensional scale of Perceived Social Support (MPSS) 7-point scale is developed by comprised of 12 items. The scale measures perceptions of support from three sources namely Family, Friends and Significant other with 4 items for each subscale.
Scoring
Each item in the scale is scored 1 for strongly disagree, 2 for strongly disagree, 3 for mildly disagree, 4 for neutral, 5 for mildly agree, 6 for strongly agree and 7 for very strongly agree. The total score is obtained by sum across all 12 items divided by 12.
Resilience scale 14: is developed by Wagnild and Young consists of 14 items. The 5 characteristics of the Resilience Scale are Purpose, Perseverance, Self-reliance, and Equanimity and Existential aloneness.
Scoring
It is a 7-point rating scale. All the items are positively scored with a minimum score of 14 and the maximum score of 98. The items are scored as from 1 (Strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree).
Procedure
The consent was taken from the higher authority of the Rehabilitation center to use inmates for the current study. The purpose of the research was clearly explained to the participant and socio demographic data was collected after taking their consent to participate in the study. The Multi-dimensional Perceived Social support Scale and Resilience- 14 scale was administered one after the other after taking short case history. After the completion of tests, tools were collected back and scoring was done as mentioned in the manual.
Inferential Statistics: Descriptive statistics, Regression analysis.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
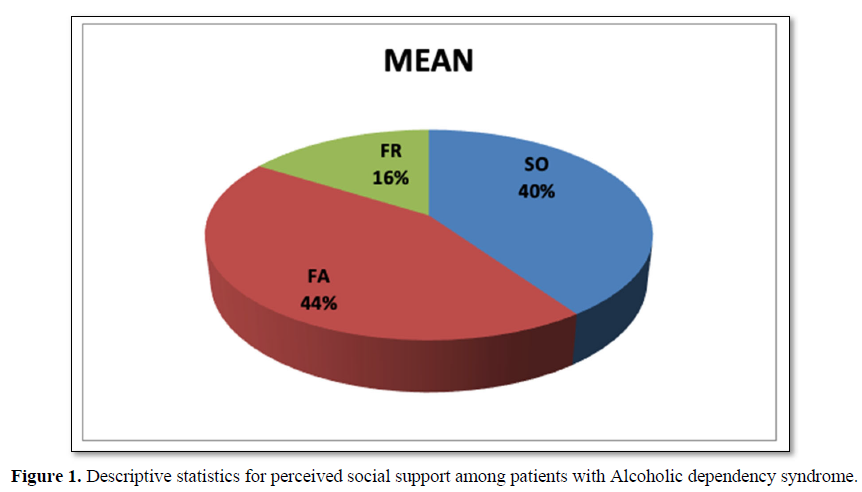
Table 1 shows the mean and standard deviation of perceived social support among patients with Alcohol dependency Syndrome. Obtained result indicates that the maximum level of perceived social support has been received from family with the percentage of 44. Patients with Alcoholic dependency syndrome perceived that the support received from the significant other of their life is 40% and least level of perceived social support has been provided by the friends with 16% (Figure 1).
This is because the research participants indicated in majority that the main etiology for alcohol abuse is from the peer influence. Initially it is with the peer’s patients used to share their joys and sorrows but gradually when they started suffering with associated disabilities (physiological, psychological, neurological and social), they started perceiving more support from the family.
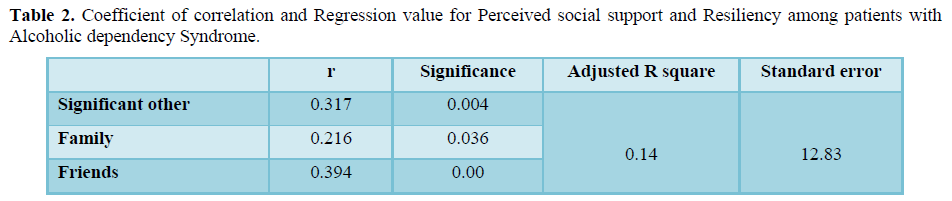
The hypothesis stating that there is no significant relationship between perceived social support and resiliency among patients with Alcoholic dependency syndrome and perceived social support does not influence resiliency among patients with Alcoholic dependency syndrome was tested using Regression analysis. The coefficient value between support from significant others and resiliency is 0.317 which indicates positive correlation, the value 0.216 indicates the presence of positive correlation between family support and resiliency and coefficient value 0.394 suggest the presence of positive correlation between support from friends and resiliency. Therefore, null hypothesis is rejected and alternative hypothesis is accepted. The regression value 0.14 indicates that about 14% of perceived social support influencing resiliency among patients with alcoholic dependency syndrome. Therefore, null hypothesis is rejected and alternative hypothesis is accepted (Table 2).
This is because in psychological disorder like ADS and other substance use disorder perceived social support play a vital role along with the pharmacotherapy. This emphasizes that the role of perceived social support helps in maximizing in one’s resiliency [12]. On the other side, study also indicating that along with the perceived social support, others factors too play a major role in enhancing the resiliency. To boost the resiliency other factor that play a major role include are personality trait of an individual, physiological and psychological aspects, level of insight on their illness, optimistic thought, positive attitude towards their life, level of achievement motivation, level of hope with regard to future, emotional maturity which they have gained from their past experience and so on [13]. Some intervention plans that are designed in the rehabilitation centers which include group and individual therapy and supportive psychotherapy also contributes to the patients to be resilient. It is also noticed that one’s motivation to overcome his or her problem also influences resiliency of an individual [14].
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
The study reveals the presence of positive correlation between perceived social support and resiliency among patients with Alcoholic dependency syndrome. It also indicated that about 14% of perceived social support influencing resiliency among them. Therefore, it is concluded that to be resilient along with the support we perceive from our society many other factors also contributes.
LIMITATIONS
- Small sample size is used in the study hence generalization cannot be done.
- Samples are restricted to only Shivamogga city.
SCOPE OF FURTHER STUDY
- The present research can be extended by comparing ADS patients with some other group.
The study can be continued with larger sample and by considering the length of rehabilitation.