Research Article
The Sea Star Asterias Rubens IGKappa Gene: Comparisons With 2 Other Sea Star Genomes from Patiria Miniata and Acanthaster Planci (Echinodermata)
4205
Views & Citations3205
Likes & Shares
The sea star IGKappa gene was cloned in 2014 by the use of primers. It was compared, in the present work, to 2 other sea star genomes: Acanthaster planci and Patiria miniata sea star genomes. A high identity, from a bioinformatic point of view, was found, with these last ones, with, a significant e-value.
INTRODUCTION
The sequence of the sea star Asterias rubens IGKappa gene was described by our team, in 2014 [1]. Since we have tried to find homologies between this gene and genes from two other Asterids: Patiria minata and Acanthaster planci. The Asterids belong to Echinodermata phylum.
We report, in the precedent paper, results obtained with these last ones by the use of blasts [2,3].
RESULTS
a. The sequence of the sea star IGKappa gene is the following [1].
a. The sequence of the sea star IGKappa gene is the following [1].
5’GGA TCC GGA GGA ATG CGTGGCAACATGGCGTCTCTATGGATGTTCTTCTT
TGTCGTGGGGATAACTTTACAACGGAGTTTGGCGATTTACACGTTTCGCG
AGCAACCGTCGGACACTAGCGCGTTGCAGGGGAGCACAGTGGTGCTTCAC
TGCTCCGTTGAGCAGTACATAAACACCACGGCCATCGTTTGGTGGAGCCG
TGACTCGGTCATCAGCCACAACAAAGACCTGAAACTGTCCAGTCTAAACA
CCGACCAGCTCCAAAGGTACTCGATTTCAGGCGACGCATCTCGGGGGGAA
TTCAACCTTAAAATAGTGAACTTTACCGCCACAGACGCCGCCAGTTACCG
CTGTCAGATG TAA GAA TTC3’
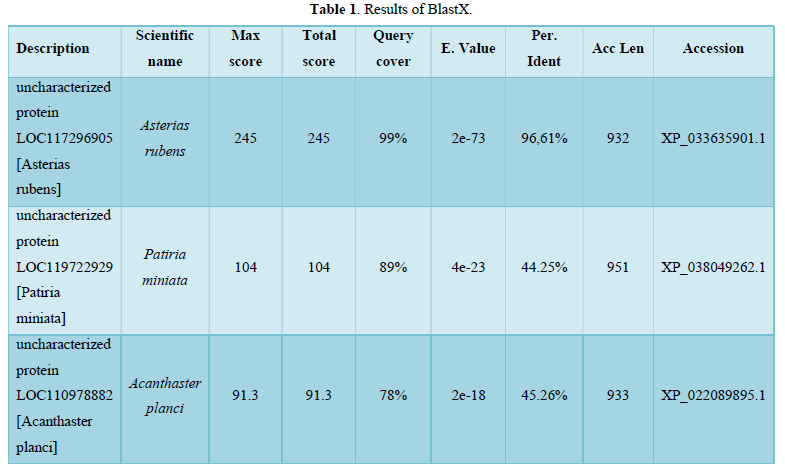
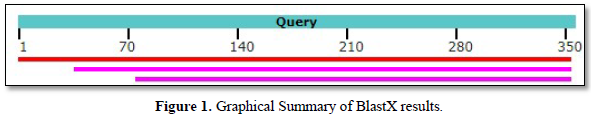
b.BlastX original sequence: BlastX results (Table 1 & Figure 1)
b.BlastX original sequence: BlastX results (Table 1 & Figure 1)
Molecule type: DNA
Query length: 357
The table allows us to obtain the following Graphic Summary (Figure 1).
- As for Alignments we observe:
97% Identities (114/118aa) with uncharacterized protein LOC117296905 [Asterias rubens] protein
Reference Protein Sequence: XP_033635901.1
Reference dna Sequence: XM_033780010.1
Length: 932 aa
Alignment: 14-131
CONCLUSION
We retain from this bioinformatic analysis, the presence of high identities between the sea star IGKappa gene and the Patiria miniata genome and the Acanthaster planci one. Recently, we have also described the Ophuirid IGKappa gene we discovered 1 month ago (Ref4): it is more evolved in terms of Immune functions.
These genes from Echinodermata (Invertebrates) bring us a new light in Immunogenetic World.


- Vincent N, Osteras M, Otten P, Leclerc M (2014) A new gene in rubens: A sea star Ig kappa gene. Meta Gene 2: 320-322.
- Marchler-Bauer A, Bo Y, Han L, He J, Lanczycki CJ, et al. (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acid Res 45(D): 200-203.
- Marchler-Bauer A, Lu S, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, et al. (2011) CDD: A Conserved Domain Database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acid Res 39(D): 225-229.
- Leclerc M (2021) Biosynthesis « De Novo » of the Ophuirid Ophiocomina Nigra Igkappa Gene. J Clin Class Immunol 1(1): 1-4.



