Research Article
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES FOR TOURISM DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A REVIEW OF TTCI REPORTS
3886
Views & Citations2886
Likes & Shares
Indian government has been taking several measures for the growth of tourism in India. Although there has been an increase in the total tourist flow but its share of world tourism remains quite low. The travel and tourism competitiveness Index report by World economic forum gives a detailed idea about the factors on which India has improved and the areas which are still needed to be worked upon. It has been claimed by the government agencies that India has become an international tourism destination. There is no denying that tourism activities indeed have grown in India over the years but the question, whether India is able to compete with the top performers on not still remains. TTCI reports suggest that there are several areas of concern for the country, before it can become a global player.
Keywords: India, Tourism, Competitiveness Index, sustainability, resources
The World Economic Forum an NGO headquartered in Geneva; Switzerland is an international organization working towards public-private cooperation. It came into existence in 1971. The forum brings together world leaders from different areas like business leaders, social leaders and political leaders to work towards economic betterment at global level, regional level and industry level. The world economic forum is committed towards improving the world scenario at global, national, regional and industry level by engaging leaders from different areas and parts of the world. It is an international organization involved in research and publication activities. The strategic insight team of the forum publishes reports of global relevance in the areas of scenario thinking, global risks and competitiveness. These reports are in-depth analysis of the variables and factors in concern. There is an extensive use of data and relevant information to give an insight on the global issues and where the countries, regions and industries stand at that point of time. These reports are widely used to understand the state at the global level and for also for course correction. These reports are also comparative studies, comparing various countries, regions, continents, industries around the world. The forum has been engaging with travel and tourism leaders for conducting in depth analysis of the tourism industry of various countries worldwide. The analysis is published in the form of a Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index report. The first report of this kind was published in the year 2007 and since then the forum has published eight such reports. The travel and tourism competitiveness Index is basically the measurement of a country’s viability to invest and develop the tourism business within its boundaries. The travel and tourism competitiveness report ranks global economies on their relative strengths in the travel and tourism business. These reports are published biennially, various policies, variables and factors are considered for in depth analysis which contributes and are important for sustainable growth, overall development and enhancing competitiveness of travel and tourism sector in the countries. The tourism stakeholders have been using the travel and tourism competitiveness index for improving the competitiveness of the tourism industry in their respective countries. This index also gives and opportunities to the economies to assess and analyses themselves at the global level. This index facilitates comparison at the world level and the countries can find out how they are performing in comparison to other countries in the world. The travel and tourism industry in India can get a clear picture of its performance at the global level by analyzing this index. This index can also act as a measurement of the effectiveness of the planning, policies, agendas, goals structured, targets set, steps taken and the implementation of the plans for the growth and development of the travel and tourism industry in the region. The factors on which the industry is doing well, the areas which need more attention, the factors in which the industry is seeing a growth, the variables in which the sector is seeing a dip, the variables on which the sector is not improving at all can all be identified using this index. However, the index has also faced criticism in the past based on the weights associated to different factors and variables and how the situations and scenarios in different countries differ from each other and they cannot be measured using same scale and variables but by far it still remains the most trusted measurement index for the global travel and tourism industry by a reliable and reputed international organization.
LITERATURE REVIEW
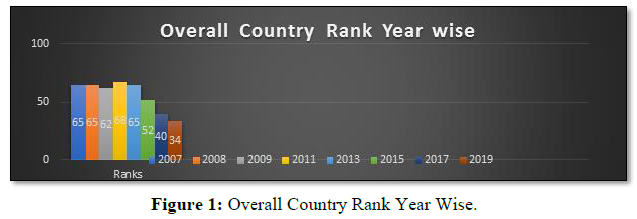
Countries today are turning towards tourism for their economic growth and progress. The governments are realizing the economic potential of tourism. It becomes the responsibility of the government to provide their citizens with better quality of life and well-being which involves better political, economic, environmental and sociocultural conditions within the country. Therefore, tourism becomes the most obvious choice as tourism growth leads to overall societal development. Therefore, studying tourism competitiveness becomes important to understand and evaluate all aspects of tourism growth and development (Crouch & Ritchie, 1999). In order to dominate the growing travel market and compete globally it is important for countries to know their strengths and weaknesses. They should be aware of their unique selling points and competitive advantages. Comparing the experiences their country is providing with other countries providing similar experiences is also important. The other thing important is to understand the tourist generating markets and the macro-environment market (Ringbeck et al., 2008). To measure competitiveness of the tourism industry a reliable and sound measurement of performance is needed. However, seeing the heterogeneous nature of the tourism industry, it is difficult to measure it in one index. Competitiveness levels for each country will be different for various sectors of the industry. Also, different regions and markets will show different levels of competitiveness. The level of complexity of model for measuring such competitiveness is bound to be high (Ring, 2016). The overall ranking of the Indian tourism industry has improved significantly from 65 in 2007 to 38 in 2019. This improvement in the ranking is majorly due to the diverse cultural and natural resources and the infrastructural development that has taken place over the years (Dahiya & Batra, 2018). Tourism competitiveness is affected by the overall human development, the theory of tourism competitiveness is a result of a relationship between capabilities and tourism competitiveness. The focus of tourism development should be on increasing tourism arrivals and revenue generations. Tourism and human development should take place simultaneously also government revenues earned through tourism should be further used to develop tourism. All this is important for designing hypothesis for theory of tourism competitiveness (Jorge, Jorge, & Shapoval, 2019). Culture is an important element of the tourism industry at any given destination. It plays an important role in developing tourism industry in the region and is one of the key elements that drive the development of tourism in the area. The countries are expected to develop strategies for tourism development according to their cultural dimensions. These strategies should only be made after having a clear understanding of the national culture. It is seen that culture is closely linked to the competitiveness of the travel and tourism industry. The national culture affects the tourism competitiveness of a destination (Kumar & Dhir 2020). Tourism competitiveness and sustainable development goals have significant positive correlation. The analysis related to tourism competitiveness index and sustainable development goals can help managers in decision making, designing strategies and focus on areas requiring attention. The index helps tourism industry stakeholders in countries ranked low to work together towards developing and improving the pillars on which the country has been ranked lower thus help in improving national economic prosperity and growth (Díaz & Fernández, 2019). In today’s times tourists apart from main attractions of the destinations are also looking for other things such as well-built infrastructure, nightlife, leisure activities etc. Tourists look for a complete rejuvenating experience. Amenities which make the travel and stay of tourists smooth at a particular destination are of equal importance and cannot be neglected at any cost. India in order to compete with destination at a global level and increase its share of total world travel has keep this in mind while promoting itself as a global tourism destination (Bhatia & Malhotra, 2012). The government has a very important role to play in the growth and development of the tourism industry. However, this involvement should be as per the requirements. For developed and popular destinations, the involvement can be minimum whereas the developing and the underdeveloped destination needs more attention and involvement from the government. The destinations which are still developing the tourism activities and those which are still exploring the opportunities for tourism development require the focus from the government (Javed & Tuckova, 2020). The tourism competitiveness of a destination is not an easy task and has to be measured from multiple dimensions. It is a multidimensional concept involving multiple factors to be taken into account. The main issues that arise with the calculation of the index are aggregation of variables, weights given to variables and duplicity of information. However, when considered at large the main factors influencing the destination’s competitiveness for tourism are air connectivity, ICT readiness and the cultural tourism resources. These are the key factors that generally lead to disparity in the tourism competitiveness of the destination (Fernández, et al., 2020).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The World Economic Forum published its first ever Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index report in the year 2007. The Index does not measure the attractiveness of a nation as a tourism destination whereas it is a measurement of the possibility of developing travel and tourism business in that country. The Index is based on analyzing a number of factors that are important for developing a successful travel business at any place, how viable it is for a country to develop tourism business. The world economic forum studies and analyses all such factors and variables for each participating nation individually to come up with a comprehensive and a compiled report of the travel and tourism competitiveness index. The index shows how attractive a country is for investors willing to invest and do business in the travel and tourism industry. Since 2007, which included 124 countries; this report has been published in 2008 including 130 countries, in 2009 covering 133 countries, in 2011 extended to 139 countries and in 2013 there were 140 countries participating for the evaluation. The recent report has been published in 2019covering 140 countries. The report analyses each country under four sub-indexes namely Enabling Environment, T&T Policy and Enabling Conditions, Infrastructure, Natural and Cultural resources. The Enabling Environment then consist of five pillars namely Business Environment, Safety and Security, Health & Hygiene, Human Resource and Labour Market and ICT Readiness. The second sub-index T&T Policy and Enabling Conditions includes four pillars namely Prioritization of Travel and Tourism, International Openness, Price Competitiveness and Environmental Sustainability. The third sub-index which is infrastructure includes pillars namely Air Transport Infrastructure, Ground and Port Infrastructure and Tourist Service Infrastructure (Table 1). The last and the final sub-index is Natural and Cultural Resources which includes two pillars namely Natural Resources and Cultural Resources & Business Travel. The report further consists of 90 indicators spread across different pillars. The report along with the scores of TTCI also includes country profile, key economic indicators by the World Bank and country indicators by the UN World Tourism Organization of each country being evaluated (Table 2). The report acts as a benchmark on which the countries can evaluate and develop its travel and tourism business in comparison to other countries in the world. The report helps in evaluating the areas on which the countries are required to work on so as to develop tourism business in the region to its fullest. The report gives an overall idea of the tourism sector in the country and helps in making investment and policy decisions. It is a source to know about the strengths and weaknesses of the travel and tourism industry in the country. The report till 2013 was divided into three sub-indexes namely T&T regulatory framework, T&T business environment and infrastructure and T&T human, cultural and natural resources and consisted of fourteen pillars namely Policy rules and regulations, Safety and security, Environmental Sustainability, Health and Hygiene, Air Transport Infrastructure, Prioritization of Travel and Tourism, Ground Transport Infrastructure, Price Competitiveness, Tourism Infrastructure, Human Resource, ICT Infrastructure, Natural Resources, Affinity for Travel and Tourism, Cultural Resources. Later on with changing scenario, industry outlook and significant changes in the framework conditions the sub-indexes were divided under four heads.
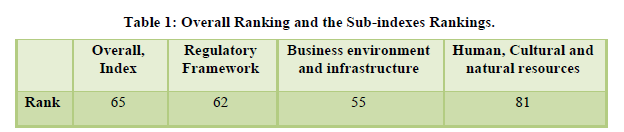



TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2007
The overall rank of India is 65 and strength of the country lies in its cultural background. The heritage and cultural sites are ranked 7thamong other economies (Table 3). The country is perceived as price competitive and is ranked 6th as the prices charged from tourists at various places is comparatively on a lower side. In the policy environment the visa stringency requirements stand at 106th position which is quiet low however the property rights are well protected and ownership of foreign individuals is authorized. Tourism infrastructure is quite underdeveloped. The marketing and branding stands at 59th position which is only mediocre, despite the aggressive efforts taken from the government in the form of promotional and advertisement campaigns and the specific efforts of the industry to promote Indian tourism destinations abroad (Table 4).
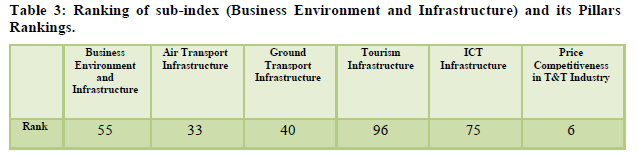
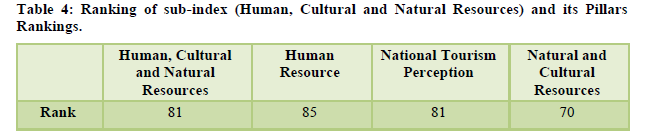
TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2008
The overall rank of India is 65th and ranked 13th for its well assessed cultural and natural resources. The country has both natural and cultural world heritage sites in large numbers (Table 5). It is ranked 20th for its price competitiveness, 35th for its air transport and 39th for its ground transport. These are satisfactory considering the country is still in a developing stage (Table 6). The tourism infrastructure still remains underdeveloped and is ranked 80th worldwide keeping in mind low availability of accommodation facilities per capita and ATM penetration as per international standards. The marketing and branding are at 51st rank even after such aggressive measures for tourism exposure and high fair participation (Table 7). The policy environment is ranked quiet low at 102keeping in mind the cost and time required to start a business, visa requirements and bilateral service agreements for air transport (Table 8).


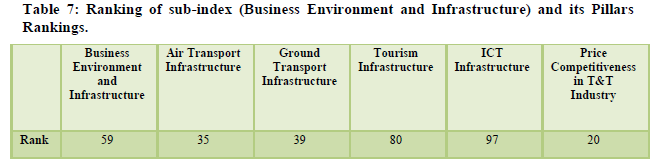
TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2009
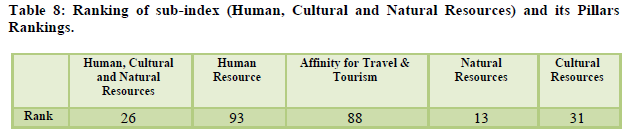
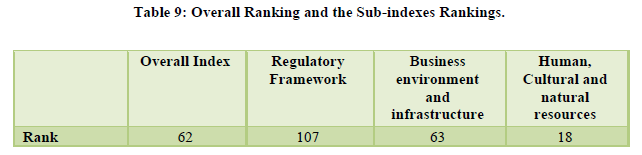
The overall rank improved by three places to 62nd. It is ranked 14th for its natural resources, 24th for its cultural resources, and 37th for its air transport (Table 9). The overall tourism infrastructure is ranked at 73rd however for its ground transport infrastructure it is ranked at 49th (Table 10). The marketing efforts of the country to promote its tourism destinations at a global level is still considered average with a ranking of 53 (Table 11). The policy environment in India has been ranked 108th which is below average considering the issues faced in starting a new business, visa requirements etc. (Table 12).






TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2011
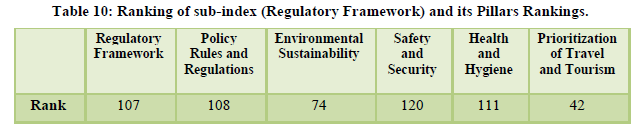
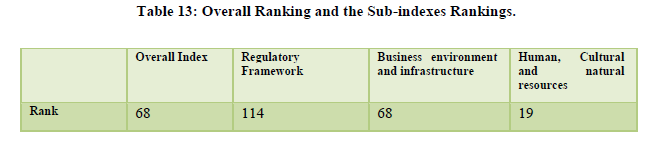
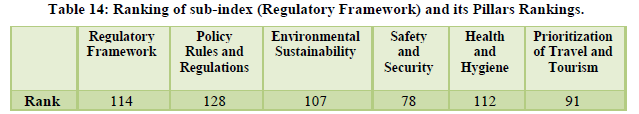
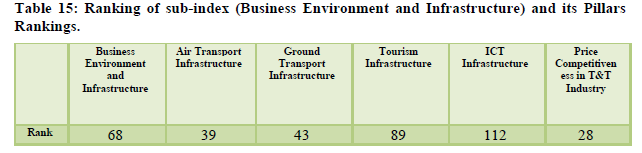
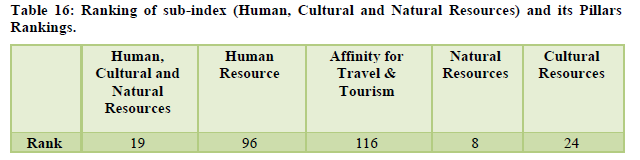
The country was ranked 68th overall with the natural resources ranked at the 8th position and the cultural resources at the 24th positions (Table 13). The diverse flora and fauna, heritage sites, culture helps the country to get higher ranks in these categories (Table 14). The air transport is at the 39th position for the year with the infrastructure for ground transport is at 39th rank however the overall tourism infrastructure still ranks 89th due to underdeveloped accommodation and ATM facilities (Table 15). The policy environment still remains an area of concern at is ranked as low as 128th along with health and hygiene at 112th position and human resource at 96th (Table 16).
TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2013
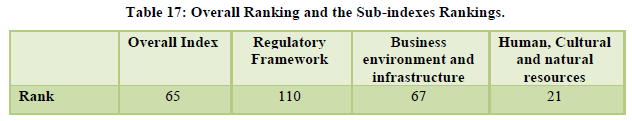
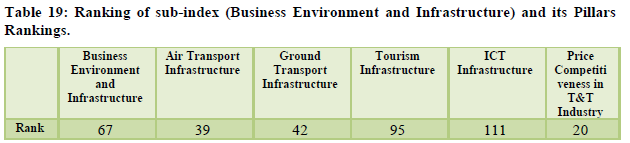
The country managed to keep to hold 65th rank overall, the natural resources were ranked 9th and cultural resources were at the rank 24th (Table 17,18). The ground transport infrastructure was given a ranking of 42 and the air transport stood at 39th position however the quality of ports was ranked 79th and the roads were on 85th position indicating the requirement for improvement (Table 19). The overall tourism infrastructure was ranked at 95th position. The other areas of concern were ICT standing at 111th rank, policy environment which was at 125th position, health and hygiene at 109th rank (Table 20).


TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2015
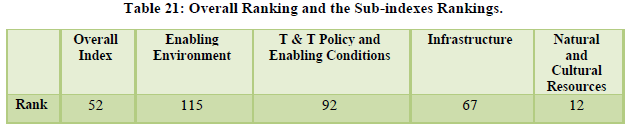
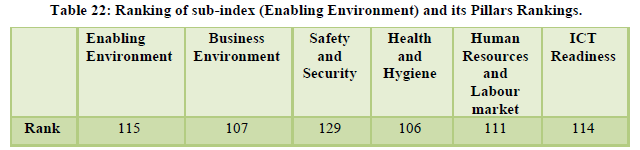
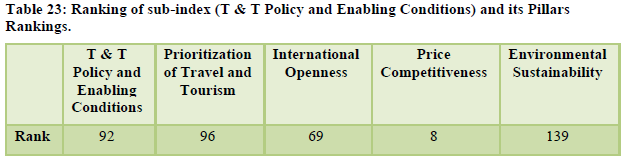
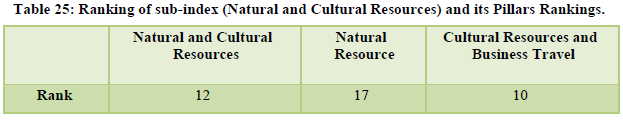
India stood at the 52nd position in the overall ranking (Table 21). The tourism industry contributes 5 per cent towards total employment in India and looking at the international tourist market the potential of tourism for further growth is quite evident (Table 22,23). The natural resources stood at 17th position while the cultural resources stood at the 10th position. However, tourism infrastructure standing at 109th position is still a matter of concern along with health and hygiene standing at 106th position, ICT readiness at 114th position, crime and violence at 97th position and environmental sustainability at 139th position (Table 24,25).

TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2017
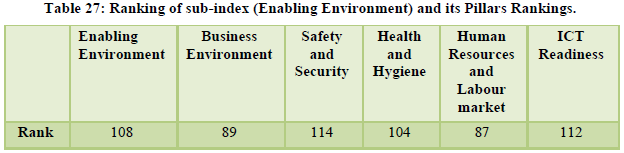
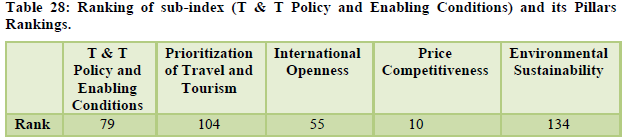
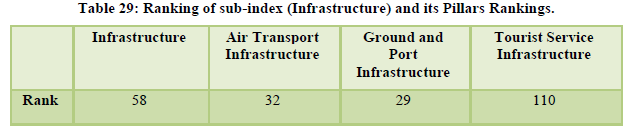
The country stood at the overall 40th position. The natural and cultural resources continue to get high ranking of 24th and 9th respectively along with price competitiveness ranked at 10th position (Table 26, 27, 28). International openness was ranked at the 55th position amid redefined visa policies and e-visa regulations. Ground transport infrastructure stood at 29th rank while tourist service infrastructure and health still remain a concern for India standing at 110th and 104th position simultaneously. The security concerns are ranked at 114th position, ICT readiness at 112th position and the human resource was positioned at 87th position (Table 29, 30).

TRAVEL & TOURISM COMPETITIVENESS INDEX REPORT 2019
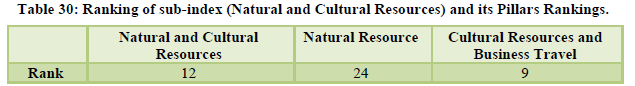
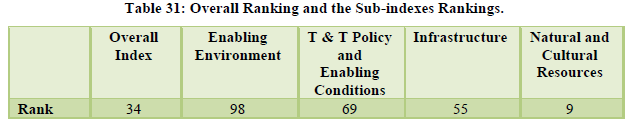
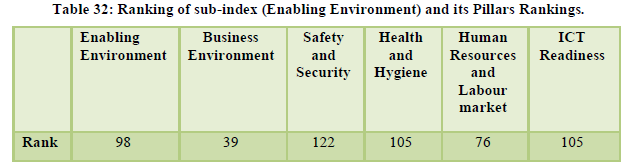
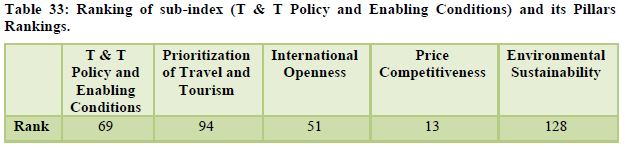
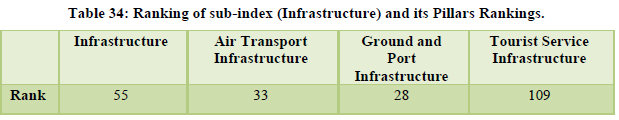
The country moved up by six places to reach the 34th rank globally. International openness was at 51st position, ground and port transport stood at 28th rank while the air transport infrastructure was at 33rd position. The natural and cultural resources were ranked 14th and 8th respectively (Table 31-Table 32). The country’s price competitiveness was ranked at the 13th position however the areas of serious concern for the country are tourist service infrastructure, environmental sustainability and enabling environment ranked 109th, 128th and 98th respectively (Table 33, 34, 35).

RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The paper is based on theoretical analysis and given data. The study is analytical and exploratory in nature. The literature review is done to understand the viewpoint of past researchers on the Travel & Tourism Index by World Economic Forum and to gain an insight on the relevance and importance of tourism destination competitiveness. The researcher believes that the TTCI index will be a good measure of tourism competitiveness as far as India is concerned. The paper analysis the TTCI index from 2007 to 2019 to understand the place of India as a tourism destination on the global level. The idea behind the research is to understand the areas where the country doing well and the areas where it is lagging behind. Looking at the magnitude at which the WEF prepares this index, the researcher suggest that the countries should use it to better use. The analysis is then used to suggest necessary measures to be taken by the tourism industry in India to upgrade itself and compete with the competitors worldwide. It is seen there is very limited research on TTCI index from India’s point of view.
RESULTS &DISCUSSION
Tourism industry has become an integral part of the Indian economy. It is one of the major service sector industry contributing considerably towards GDP, foreign exchange and employment generation. It is important for the government to develop and support the industry. The travel and tourism competitiveness index is a performance benchmark for the Indian tourism industry. As the index measures the performance of the industry on various parameters therefore it should be used by the private and the public sector for important decision making and analysis. As the index suggest areas where Indian tourism industry is doing well and where there is a need for betterment thus policy makers and service providers should refer to this index and work towards the betterment of the industry. Travel and tourism competitiveness index will help the Indian tourism industry to get an insight on its overall performance and where it stands on the global level. When we talk about increasing our share of world tourism, we will have to make sure that our tourism destinations and tourism products are at par with the major tourism destinations worldwide. The index can help the tourism professionals and policy makers to focus on areas where the country is lagging behind and take necessary measures to improve its performance. India has always been a destination for tourists interested in natural and culturally inclined destination. The diverse cultural and religious background with large number of heritage destinations, different languages and dialect, diverse food and clothing styles has kept its popularity intact among the tourists. Varied flora and fauna make it a paradise for nature lovers and tourists looking for solidarity. The country as a tourist destination is price competitive and is value for money. The tourists in large numbers are able to afford travelling to India as compared to other destinations globally. Over the period of time the tourism destinations in India are becoming accessible to the tourists with improving air and ground transport system. However, the overall tourism infrastructure is still a problem for the country with concerns regarding accommodation facilities and amenities such as ATMs etc. The country is not considered fully safe for tourists and is ranked quiet low in safety and security. Environment sustainability is a challenge for the government with over commercialization and decreasing carrying capacity. Health and hygiene is again a concern point for tourism policy makers. The government is promoting the ease of doing business and supporting budding entrepreneurs through various schemes, exemptions and relaxation. There are schemes to attract foreign as well as domestic investors but still business environment is placed quiet low in the ranking table. It still needs improvement to attract potential investors. The government although seems quite serious towards developing tourism activities in India but it still hasn’t prioritized tourism industry to that level, other countries globally are seen focusing and emphasizing more on tourism growth and development. ICT readiness is again a factor of concern for the country. The country still ranks below average in technological advancement of the tourism industry. Even after launching the mighty Incredible India Campaign in 2002, the advertisement effectiveness quotient still remains low. In the era of digital marketing, social media and other technological advancements the Indian tourism industry needs to catch up with its global competitors. Although there are a number of factors which needs attention of the industry professionals and government of India but still the overall rank has improved considerably over the past few years (Figure 1). The improvement in rank is seen as a result of improving ground and air infrastructure, price competitiveness, diverse cultural and natural tourism destinations and promotional campaigns also playing some role in it.
The graph suggests that the overall rank of India is improving over the past few years. India has so much potential to further develop tourism activities and keeping a check on its TTCI index will only help. The government and tourism professionals can really use this index for future planning and decision making. This index also acts as a reality check for the tourism industry professionals and tell them where they stand globally. India tourism industry has shown improvements year on year but still a lot of work has to be done to stand among the global leaders. The
country is still lagging behind other countries on some parameters. To increase its share of world tourism arrivals and receipts the country has to work on these parameters and try for betterment.
CONCLUSION
Although the overall performance of the Indian tourism industry is improving globally however there are certain parameters that cannot be overlooked and they are a necessity for improving tourist experiences at various tourism destination in India. Tourist infrastructure including accommodation facilities, banks, sewage and sanitation and other basic amenities has to be developed at all tourism destinations. Ease of doing business is again a parameter which the government has to focus, licensing and approvals should be given without any hassle and the entrepreneurs in the industry should be supported and welcomed to do business. Another factor that needs attention is safety of tourists, it should be of primary concern because if the tourists will not feel safe, they will not come. The country should also focus on improving international openness and ICT infrastructure of the industry. Lastly environment protection should not be overlooked as Indian tourism thrives on its diverse flora and fauna along with its cultural heritage and if the environmental conditions get deteriorated, the country will lose its most important tourism asset.
LIMITATIONS
The paper is only focusing on TTCI index as a benchmark for assessing the performance of tourism industry in India. It is a study the TTCI index over the past 12 years in reference to India. There can be other indexes assessing the performance of the industry which can also be used.
SCOPE FOR FUTURE RESEARCH
The researchers can further build on this paper and draw ideas to use the index for the betterment of the tourism industry in India. There can be other indexes assessing the performance of the industry which can also be used. This being a theoretical study can be converted into an empirical study through primary data collection such as interviews and opinions of tourism professionals on the importance of this index and its practical usage.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The paper is a result of the co-operation and equal efforts from all the co-authors. Without mutual understanding and respect, it wouldn’t have been what it is.
- Crouch, G.I., & Ritchie, J.R.B. (1999). Tourism Competitiveness and Societal Prosperity. Journal of Business Research 44(3), 137-152.
- Ringbeck, J., Gross, S., Chiesa, T., & Blanke, J. (2008). Improving Travel and Tourism Competitiveness. Trends and Issues in Global Tourism, Springer Berlin Heidelberg 97-108.
- Ring, A., (2016). Alternative models within the framework of the World Economic Forums Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index Suggestions for theory development. Travel & Tourism Research Association Advancing Tourism Research Globally 42.
- Dahiya, K.S. (2018). India Sustainability and the Tourism Rankings. African Journal of Hospitality Tourism and Leisure 7(3).
- Ridderstaat, J., Croes, R., & Shapoval, V. (2019). Extending tourism competitiveness to human development. Annals of Tourism Research 80, 102825.
- Kumar,S., & Dhir,A.(2020). Associations between travel and tourism competitiveness and culture. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management 18,100501.
- Diaz, B.R., & Fernandez, J.I.P. (2020). Sustainability as a Key Factor in Tourism Competitiveness A Global Analysis. Sustainability 12(1), 51.
- Bhatia, B., & Malhotra, N. (2012). Critical Appraisal of Aspect of Attractions for Tourist Destination Competitiveness of India and Singapore. International Conference on Trade, Tourism and Management (ICTTM) 21-22
- Javed, M., & Tuckova, Z. (2020). The role of government in tourism competitiveness and tourism area life cycle model. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research 997-1011.
- Fernandez, J.A.S., Azevedo, P.S., Martín, J.M, & Rodriguez Martin, J.A. (2020). Determinants of tourism destination competitiveness in the countries most visited by international tourists Proposal of a synthetic index. Tourism Management Perspectives 33, 100582.


