6
Views & Citations10
Likes & Shares
DISCUSSION
The term "metaverse" first appeared in Neal Stephenson's 1992 science fiction novel "Snow Crash." It combines the Greek word "meta," meaning "beyond," with the word "universe," which refers to the world or the cosmos [2]. So far, there is not a perfect definition for the term 'metaverse', but it is generally understood as a virtual digital space that is a version that exceeds the real world. Users, individuals in the metaverse, create avatars to represent themselves, and they engage in various activities. Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Virtual Reality (VR), and Augmented Reality (AR) are selectively used to enable more elaborate and realistic interactions with other users. As a result, the metaverse is capable of reaching different kinds of markets and the interests of many people, which leads to rapid growth in the metaverse population [3]. However, the rapid development of the metaverse means the individual activities and capabilities within the metaverse increase the possibilities of more legal issues. The legal problems within the metaverse are categorized into two types, and the first is the cases where crimes that are happening in the real world are also occurring in the metaverse. Regards to these cases, the key question is, whether the existing laws and regulations effectively facilitate the metaverse. Second, legal issues that newly arised only due to the virtual nature of the metaverse. In this case, it should be discussed whether the gaps in regulations for these new problems exist. Some generic examples of legal issues in the metaverse include verbal abuse, discrimination, and sexual crimes between users. In addition, financial crimes such as virtual assets ownership disputes, fraud, and gambling, as well as issues related to intellectual property rights can be brought up in the future [4]. On the other hand, risks in the metaverse may not only come from users but also from platform providers. Some companies may monopolize the digital market related to the metaverse, violating existing competition and antitrust laws, such as the Unfair Competition Prevention Act, and privacy and security issues may arise due to the extensive collection of information [5]. Despite the existence of potential problems in the metaverse, discussions about the regulations for the metaverse are still in their early stages. Therefore, it is required to establish legal frameworks to protect the users’ rights and to consider ways to regulate the issues occurring in the rapidly growing metaverse.
REGULATORY AMENDMENTS IN SOUTH KOREA
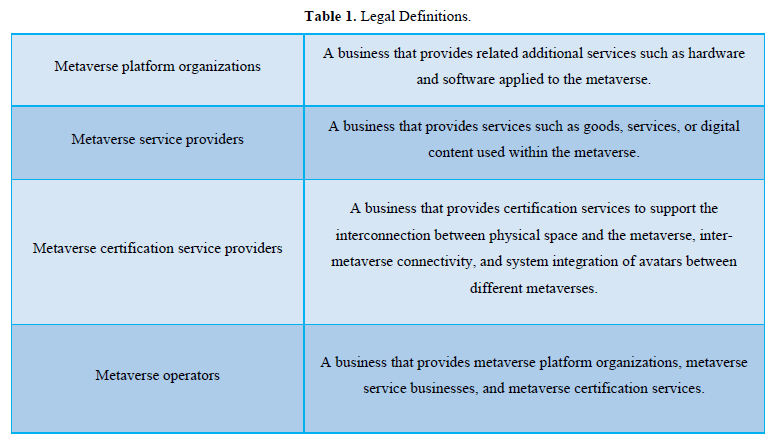
In South Korea, a pan-government strategy was announced to deal with innovation in the metaverse, and the Act on the Promotion of the Virtual Industry Promotion Act has been discussed steadily. Following the pan-government strategy on the metaverse, the legislation was approved at the Cabinet meeting in February 2022, and it will be implemented initially in the world in August 2024. According to the legislation, the metaverse is defined as a virtual space or a combined space that enables economic, social, and cultural activities based on technologies that extend the metaverse user’s senses into the virtual realm or the real world to facilitate interaction between individuals and digital information [6]. Moreover, the legislation offers an in-depth explanation of metaverse concepts that embody metaverse platform organizations, metaverse service providers, metaverse certification service providers, metaverse operators, and metaverse users (Table 1).
Additionally, the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) is required to establish a basic plan for the activation of the metaverse, supporting the metaverse industry and stabilizing the experiences of users, every three years. The Minister of Science and ICT shall finalize the plan through the established committee to deliberate on related matters. It also mandates the responsibilities of metaverse operators, and the operators who want to form metaverse platforms or service organizations are obligated to inform the Minister of Science and ICT of the establishment of the metaverse industry. Metaverse platform organizations are obligated to provide a stable metaverse connection and to create an environment that facilitates metaverse users to decide their own disposition of their avatars and virtual assets. There are also supportive policies for encouragement, protection, and fosterage of the metaverse industry, and the government shall establish metaverse action plans and award prizes to excellent organizations. It also stipulates that a dedicated agency related to the metaverse industry shall be designated so that related policies can be promoted. Furthermore, it is informed that personal information and intellectual property rights should be protected for metaverse users [7]. Like this, South Korea has established a legal basis to promote the development of the metaverse industry and protect the rights of metaverse users.
CONCLUSION
The metaverse affords individuals the chance to acquire a range of experiences in advanced digital technology. As the metaverse advances, its users expand quickly, prompting concerns over legal issues concerning illicit behaviors within the metaverse. However, the on-going legal dialogue on this topic remains inadequate.
On the other hand, South Korea is actively promoting regulatory reform in compliance with related legislation to promote the development of the metaverse industry and protect the rights and interests of users. This practice in South Korea is able to be one of the progressive legislation examples due to the limited regulations concerning the metaverse globally. As the legislation emphasizes self-regulation of the metaverse, which is considered a public sphere, it could lead to expedited settlement of disputes and growth of the metaverse industry. However, the important thing to consider is that as self-regulation is implemented without legal effect or binding force, unlike public regulation, there is the possibility of confusion in the application of the law as legal regulations. Besides, it needs to be discussed with additional studies about whether to deal with the legislation of the metaverse in terms of pre-regulation or post-regulation.
- Jaeun H, Kyunglyul L (2022) Limitations of Modern Criminal Law and Provision of Future Criminal Law in Metaverse - A current view for the enactment of the meta-criminal law. Korean J Cri 34(3): 67.
- Myoungseob M, Myungsoo K (2022) Study on the Role and Legal Responsibility of the Metaverse Platform in the Age of Virtual Economy. Korea Institute Intellectual Propert 32(4): 146.
- Haesung Y, Joontag C, Suk-young J, Sungmin P, Kyoung RY, et al. (2023) Legal and Policy Responses to New Mechanisms in the Metaverse Era (Ⅰ). KICJ Res Rep 21(143): 22-24.
- Jinkyu L (2021) Metaverse, Privacy, and Ethics - Preparing for the Beginning of the Discussion. KISA Report: 2.
- European Parliamentary Research Service (EPRS) (2022) The metaverse: opportunities, risks and policy implications. European Parliamentary Research Service. Available online at: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/cmsdata/268589/eprs-briefing-metaverse_EN.pdf
- Ministry of Science and ICT(MSIT) (2022) MSIT to announce pan-government strategy on metaverse. Available online at: https://www.msit.go.kr/eng/bbs/view.do?sCode=eng&mId=4&mPid=2&pageIndex=&bbsSeqNo=42&nttSeqNo=621&searchOpt=ALL&searchTxt
- Hojun J (2024) Virtual Convergence Industry Promotion Act' Decided by the State Council Establish promotion plan every three years and support commercialization. Maeil Business Newspaper. Available online at: https://www.mk.co.kr/en/it/10946959
QUICK LINKS
- SUBMIT MANUSCRIPT
- RECOMMEND THE JOURNAL
-
SUBSCRIBE FOR ALERTS
RELATED JOURNALS
- International Journal of AIDS (ISSN: 2644-3023)
- International Journal of Surgery and Invasive Procedures (ISSN:2640-0820)
- Oncology Clinics and Research (ISSN: 2643-055X)
- Journal of Spine Diseases
- International Journal of Clinical Case Studies and Reports (ISSN:2641-5771)
- International Journal of Anaesthesia and Research (ISSN:2641-399X)
- Journal of Renal Transplantation Science (ISSN:2640-0847)

