Research Article
AN ASSESSMENT OF SERVICE QUALITY GAP ANALYSIS OF JALDAPARA NATIONAL PARK THROUGH IMPORTANCE-PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS (IPA) MODEL
3444
Views & Citations2444
Likes & Shares
Purpose: This research concentrates an analytical conclusion of the implication of IPA model in the sector of tourist perceived service quality. The researcher implemented the IPA model to assess the most effective performance determinants in the making of tourist satisfaction. Jaldapara National park attracts a number of tourists for its wildlife scenery and the number of tourists is increasing from the last few years. It is notified by most of the researchers that some of the national parks have failed to meet the expectation of tourist perception. The Jaldapara national park is one of the significant vacationer goals in West Bengal and this paper is attempting to assess solid significance-execution factors with the utilization of IPA model.
Design/methodology/approach: Research is principally founded on a mix of qualitative and quantitative methods. A qualitative methodology changed into broadened data of the significant experience of administration remarkable components which has the most significant impacting factors in explorer goal fulfillment, quantitative research consolidated the dimensions importance-performance analysis model. To fulfill expected research objectives a modified research questionnaire was used with suitable sample collection. SPSS.20 was used to calculate research findings.
Findings: The empirical analysis confirmed that some of the variables like some of the variables like ‘Staff are well trained and knowledgeable’, Availability of the park information(online/offline)are well informed and Park protection & safety are nicely ready, have high significance and low overall performance. Result also shows the demographic profile of the tourist choice of destination towards Jaldapara national park.
Practical implications: Analysis of the result has an effective managerial implication which can create destination branding to attract tourists from other states. Industrial managers and Government entities need to be empowered and maintain tourist expectation towards this national park and must create some concentrated other influential factors which possess some high performance and some low expectations factor. In future some of the other attributes can be added like the economic factor of the tourist and tourist motivation can be analyzed. The research can be explored with a comparative analysis with two or more national parks on time.
Type of the paper: Research
Keywords: Destination Service Quality, Importance-performance Analysis, National Park.
INTRODUCTION
The Jaldapara wildlife sanctuary was established in the year 1941 to protect Indian one horned rhinoceros and from 2012 it was declared as a national park (Indian Express, 2020). Tall elephant grasses cover most of the forest. The Jaldapara national park is a major ecotourism attraction in West Bengal and also boosts the state economy. In addition, the responsibility for the conservation of nature the National Parks authority is responsible for generating revenue for the economy, which is beneficial and protection for the local communities at the same time it provides tourist satisfaction (Said, Shuib, Ayob & Yaakub, 2013). Like in other business sectors, the tourism sector also focusing on service quality for winning competitive advantage among others. The research consciousness on perceptual development at the provider quality it truly is considered as a critical aspect to reinforce tourism place fulfilment (Hudson & Miller, 2004). Service quality performs an important function which accounts for a significant level of tourist satisfaction and Ensures the revisit intention towards a destination through creating a positive word of mouth (Tak, Wan & Ho, 2006). The estimation of perceived service quality is an important parameter to understand tourist attitudes towards the destination and it helps to make marketing strategy more effective to promote tourism (Birenboin & Shoval, 2013). Birenboin et al. (2013) state that pricing and the tourist attraction nowadays are not considered important factors which make tourist attraction towards destination. It is now so important for management and also for a researcher trying to identify the more relevant factor which can help for making an effective marketing strategy to boost national park revenue.
This paper seeks to achieve two vast objectives specifically to identify the viable primary attributes. which can be influencing the choice of the national park as a visitor vacation spot and secondly, we are attempting to analyze the gap of perceived service quality of Jaldapara national park. The impact of growing the service quality of the gap is suited to the base and promoting their strategies for the acknowledgement given to the tourist and tourism services of the city to the desires of the entice vacationer.
LITERATURE REVIEW
The Jaldapara national park is a well-known tourist destination situated near Eastern Himalayan in Alipurduar district. This national park spreads over about 217 square kilometers and has several forest attractions. Every year a growing rate of domestic in addition to international vacationers arrives which improve the state financial system. Several private hotels and restaurants are now engaging in providing service to tourists. It's miles now crucial to degree the space of carrier best the of this countrywide park so that nearby coping with authority figuring out possible important measurement dimensions and reforming for prevailing an aggressive benefit inside the extension growth of the home financial system. Imparting excessive exceptional of provider making sure traveler pleasure is an important component and diagnosed all around the global inside the tourism area (Stevens, 1995).The academic researcher developed several models which deal with service quality gap between exception and perception level of service, with respect to service and to identify the appropriate variables of ‘service quality’ with specifying to the essence of service provider. The various academician and service sector research academics used ‘SERVQUAL’ model to measure the level of service high-quality with the help of five dimensions specifically “tangibles, reliability responsiveness, assurance and empathy”(Parasuraman, Zeithmal & Berry, 1988). Major significant research accomplished of the tourism industry have been done by the utilization of the SERVQUAL model (Fick & Ritchie, 1991). Result validates that SERVQUAL has all sets of latent instances of several service segment which carries in the tourism sector. Apart from the SERVQUAL model some of the researchers suggest some other important service quality measurement models which are widely accepted in the tourism sector. In creating satisfaction (SERVPERF) instruments are well practiced by several researchers in the tourism sector suggested by Cronin and Taylor (1994). Research reflected that in the tourism service sector SERVPERF scale can be more effective in making comparative strategy then comparison with SERVQUAL (Hudson et al., 2004) to include measurement of service quality within the tourism industry employing three-dimension fashions specifically; IPA, SERVQUAL & SERVPERF which plays the first-rate contribution. The verdicts advised that the sequence of the three models namely, SERVQUAL & SERVPERF & IPA are acknowledged equally relevant in containing service quality in the tourism industry in India. With a purpose to evaluate the strongest performance elements in traveller delight (Enright 2004; Vassiliadis 2006; Zhang 2004) emphasis IPA model proposed through Martilla-James(1977) one in every of most important and substantially everyday utility in the tourism sector. There are two broad areas of customer traits in the IPA model: ‘Importance to customer and performance level of in delivery’ (Martilla-James, 1977). Taking a gander at the travel industry contributions, IPA is utilized as an incredible asset in the travel industry making arrangements for destination. Going before research utilized IPA in settings alongside: Lodgings (Babic-Hodovic & Arslanagic-Kalajdzic, 2017; Hoovic, Kalajdzic, Bandas & Sivac, 2019), the results affirmed a moderate prevalence of the IPA conceptualization over that of SERVPERF in anticipating fulfillment and in influencing client attitudinal and conduct results. This examination additionally affirms the significant intervening capacity of fulfillment on buyer results. Gainful assessment additionally completed in Taiwan which analyzes the investigations of Mainland China and Taiwan guests at a historical center and their impression of understanding transporter first-class. IPA to find transporter factors vital to the excellent of exhibition hall translation for guests from Mainland China and Taiwan (Cheng, Kuo, Chang & Hu, 2019).
As observed in Figure 1, there are four quadrants in the IPA model with two-segments low and high. and each quadrant is divided with these low and high parameters. In the vertical axis we are measuring the importance attribute of the service quality and the performance of attributes in the horizontal axis (Martilla & James, 1977).
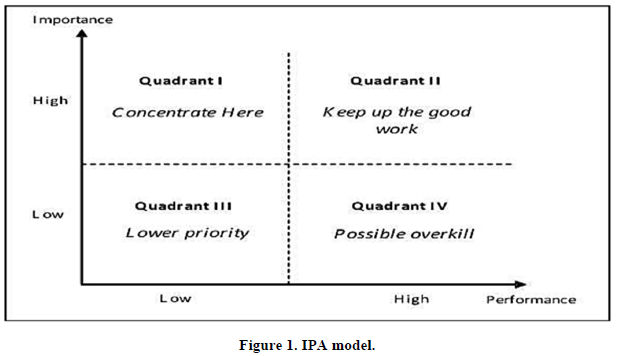

IPA model is proposed by Martilla & James (1977). Nature and technique of IPA model which is easy to handle and allowed to use in the different tourism sectors by different organizations for making long term marketing strategy by understanding important effective factors. (Hansen, 1999). A reliable perception of visitor behavior could be a determining portion which promotes national parks to enhance their command over marketing which draws and gains customer satisfaction (Kamenidou, 2009; Vassiliadis & Chiappa, 2013). Research shows in the context of the national park, tourist perceived service quality along with its safety & security positively correlated with tourist satisfaction for making revisited intentions. (Pikkemaat, 2006; Tsang, 2012). The method of measuring important factors of service quality which may improve organizations to accept the tourist perceptions, and it also helps to determine their requirements through expectations (Arabatzis & Grigoroudis, 2010). In Hong Kong, a contextual examination with 26 hotels done by Chu & Choi in the year 2000 showing that importance and performance attribute as perceived by any business and recreation explorers. Results of four quadrants helps marketing managers for making destination strategy namely destination branding. Application of IPA model also used to understand visitors' motivation towards a national park in Tanzania’s (Wade & Eagles, 2003). To understand the quality of service gap, so much research has been continuously progressing but SERVQUAL fails to provide an explanation of strategic implementation for continuous enhancement in the area of service quality measurement. Furthermore, the researcher acknowledges that uses of IPA analysis can be an efficient determination model in future to experience effective variables for enhancement or affirmed of service quality strategy in national parks. Previous research evidence of other studies also showing incompetent to understand the dearth of the managerial association of IPA model in the context of the Indian tourism industry.
Research gap
Knowing the size of the two measurement determinants knowing ‘significance and overall performance’ of service exceptional gap analysis for the tourism industry (National Park Indian Tourism) could be an independent novel initiative. The managerial assumption of IPA model and its influence on tourist satisfaction for creating decisive word of mouth has never been questioned in graphical representation has a very recently connection.
Provider satisfaction in the situation of the enterprise of journey and tourism in isolation (namely for a National Park in West Bengal tourism).
Objective of the study: From the extensive studies of the literature review, the researcher wants to identify the following objectives of the examined study are
- to discover foremost attributes of the Jaldapara national parks from the tourist perspective.
- to understand gap of the service quality through the implication of IPA
- to identify differences in importance-performance in the context of demographic differences among the tourists in Jaldapara.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The past examination was directed with the assistance of the SERVQUAL model yet none of the exploration has been led with the use of the IPA model in Indian the travel industry setting to comprehend administration quality data on the recreation center. Utilization of IPA variation on this association is broadly acknowledged due to recognizing and readiness of crucial by and large execution factors that make purchaser delight (Enright et al., 2004). Estimation of administration quality is essential for making and improving advertising procedure for a national park in India.
A mixed model of (Qualitative and Quantitative) strategy was applied for this exploration. A subjective strategy changed into sent inside the setting to perceive the basic qualities of the national park which charge explorers toward goal and vacationer desire from the administration viewpoint. Quantitative exploration was utilized to distinguish the dimensionality and unwavering quality of the scale utilized for significance for the recreation center and execution of the recreation center. The quantitative strategy turned out to be to a great extent used to perceive the transporter administration quality hole examination through the IPA form. Earlier consent was acquired from the recreation center authority before approaching any inquiry for the vacationer. To assess vacationer conduct and administration quality, a poll was developed essentially dependent on going before contemplates (Taplin, 2012). We utilized a comfort inspecting strategy which is anything but difficult to apply in this investigation.
The past examination dependent on the important point in the section of writing audit and a pilot study was led before determination in test size and inspecting strategy in a significant place of interest in West Bengal. For the size of the sample we utilized the Taro (Yamane, 1973) equation with 95% certainty level. (as per WBTDC complete 1250 approx. vacationers showed up in the year 2018 between July and August ) The figuring equation of “Taro Yamane is introduced as follows n=N/1+N(e)2” n= test size required N= no of individuals in the populace e= reasonable mistake in % n=250/1+250(0.05)2 n=150 (approx). All out 150 surveys were disseminated among the travelers who can at any rate remain 24 hours in Jaldapara national park. A systematic random sample was taken for a sample survey.
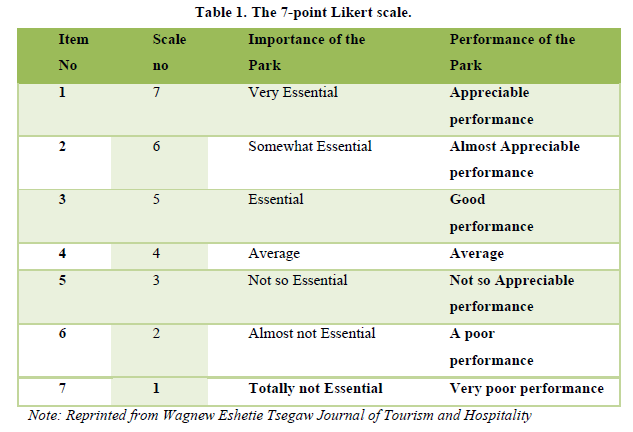
Jaldapara national park, a remarkable get-away goal objective has been decided for the examination. A changed IPA model Proposed By (Martilla & James, 1977) has been used for this investigation work. The review gets disengaged into moieties other than the part engaged at the demography of the interviewees. The principle half changed into theoretical and changed into focused on making aptitude of the major properties of the Jaldapara countrywide parks from the explorer’s edge. The observers had been approached to rate their extensive level in and searching the objective and its characteristics particularly (a) Criticalness of the amusement place and (b) Execution of the entertainment community. The second piece of the review was dealt with utilizing a formed study. A 7-factor Likert scale creates to be applied. The survey contained scaled (7 focuses Likert scale) matters to have information of the dimensionalities of the point. For the point of view structure and data test, a SPSS 0.20 got applied.
- Measurement of the factor construct
To measure the tourists’ behaviour on service quality and association quality, a shrouded pool of 14 things were adjusted from literature (Martilla & James, 1997; Chien, Hong, Sheu & Hung, 2011; Tsegaw, 2017). The analyst chose to wrap up the pool of things assessing the vitality and execution of things which impacts guests essentially after the substance evaluation of hypothetical get-togethers.
RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE DATA
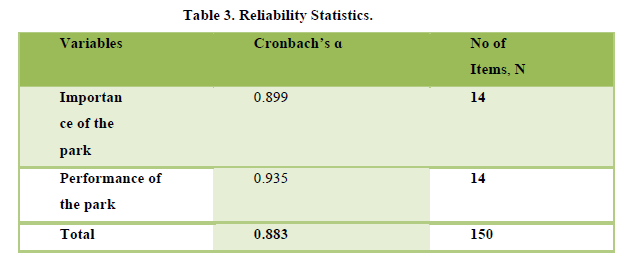
An exploratory factor analysis with varimax pivot transforms into crossed on to assess the dependability (De Vellis, 2003) and make a build validity (Netemeyer et al., 2003) with a 150 example length. The things having issue loadings lower than 0.6 or move-stacked on various perspectives had been disposed of. The inward consistency and ceaseless great injury up being enormous as Cronbach's alpha appeared as >0.7 (Hair et al., 2006). While 14 issues have been accumulated on Bartlett’s investigate sphericity (a genuine investigation of the closeness of associations of a large portion of the factors) and the KMO (Kaisere Meyere Olkin) amount of looking at sufficiency had been evaluated to consider the factorability of the records. In this examination, content fabric realness depends absolutely upon writing evaluation and expert sentiment (Malhotra, 2006; Mc Tavish, 1997). Records acquired from examinations dispatched to seven pros comprehensive of dwelling managers and academicians and gives off an impression of being a crucial assessment device in putting aside explorer direct.
The KMO (Kaisere Meyere Olkin) proportion of testing samples had been estimated to evaluate the factorability of the records. The KMO feet at 0.883 surpasses the best possible least assortment that is 0.6 (Hair et al., 2006). The Barlett’s register of sphericity turned out to be great measured (Chi-square-1265.654, df=one hundred sixty, 0.000 p<0.00). The Cronbach's alpha score of unwavering quality extended from 0.899 to 0.935 (Table 1). To accomplish a more prominent great measured and interpretable final product, a few things which stacked on more than one thing had been erased.
Data analysis
The total data was investigated in the wake of coding, utilizing the SPSS for Windows. The technique for information investigation is as per the following. To start with, to characterize demographic data for the respondents to the questionnaire, a frequency analysis examination was directed. Second, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient, which is a measure of internal consistency between queries, was determined to assess the reliability of the scales (Table 2). Both alpha coefficients were above the 0.7 cut-off point, suggesting that each build had a reasonable degree of reliability. Third, exploratory factor analysis was performed to assess construct validity. The results of the exploratory factor analysis are given in Table 3. Fourth, to verify the significance and performance through the IPA matrix of Jaldapara National Park service quality.


Demographic profile
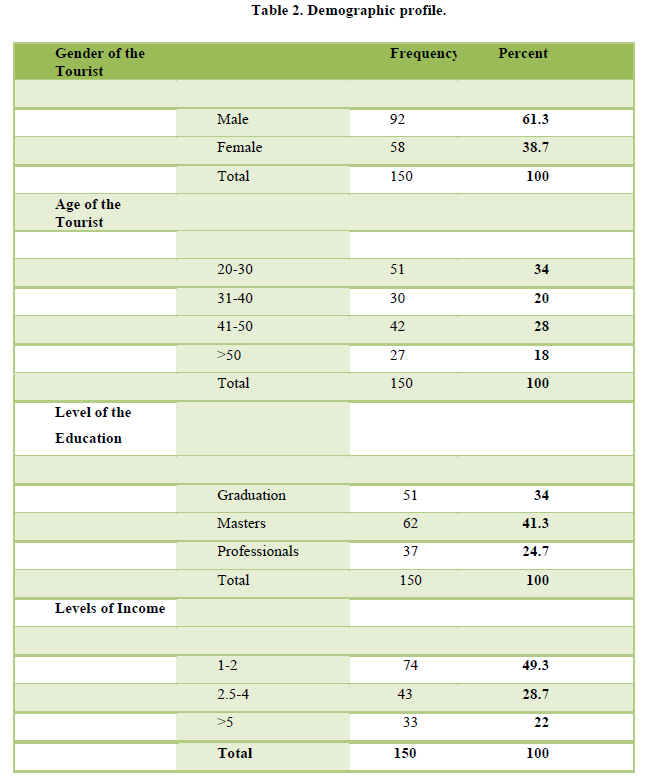
By the use of SPSS 20,the overviews results are indicating that ninety-two are male i.e., 61% are male and fifty-eight female. 38% are female respondents. In terms of age 34% are between 20-30 years, 20% are between 31 to 40 years old and 21% tourists fall under the age group 41-50 years old and only 18% fall under above the age of 50. Regarding level of education most of the tourists almost 41% are holding graduation degrees and 34% are post graduate level with 24% are from professionals pass out. In terms of income most of the tourists 49% income group falls under 1 to 2 lac and only 22% holding more than 5 lac income. The survey reports are showing that 87% of tourists were the first-time visitors of Jaldapara national park and 9% had been in the park once before whereas only 4% previously visited the place twice. In terms of accompanied by partners 75%, staying with family 21% and only 4 % among tourists are staying alone.
From Table 3, we can understand four major important variables for tourist in the park in basic ‘the direction of park map is well viewed (6.90), park safety & security are well equipped (6.28), parks are well maintained (6.21) and information from online and offline for the park (5.84). Four least important first-aid treatments are well available (3.5), location is the value for money (3.45), park conservation is well maintained (4.11), viewpoint location is well area (4.58). As a viewpoint of performance side park has very good performance of direction of park map (6.48), the scenery and unique natural features are well maintained (6.4), staff are well behaved ready to help (5.83), park safety & security are well equipped (5.8). Similarly, park has least performance scale like first-aid treatments are well available (3.1), park conservation is well maintained (3.14), location is value for money (3.24) (Table 4).
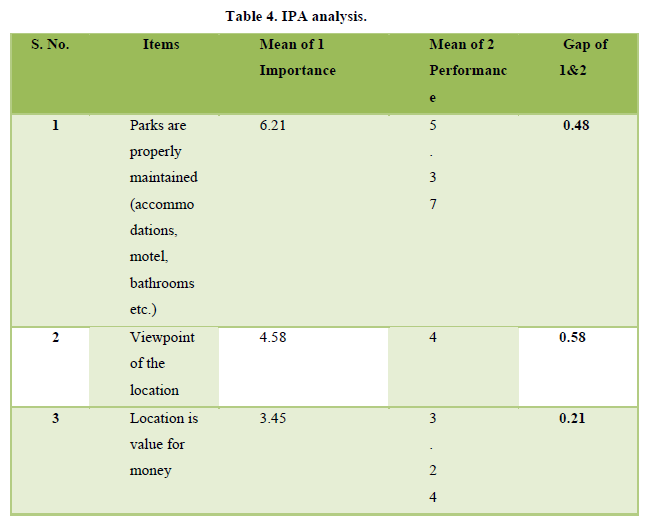
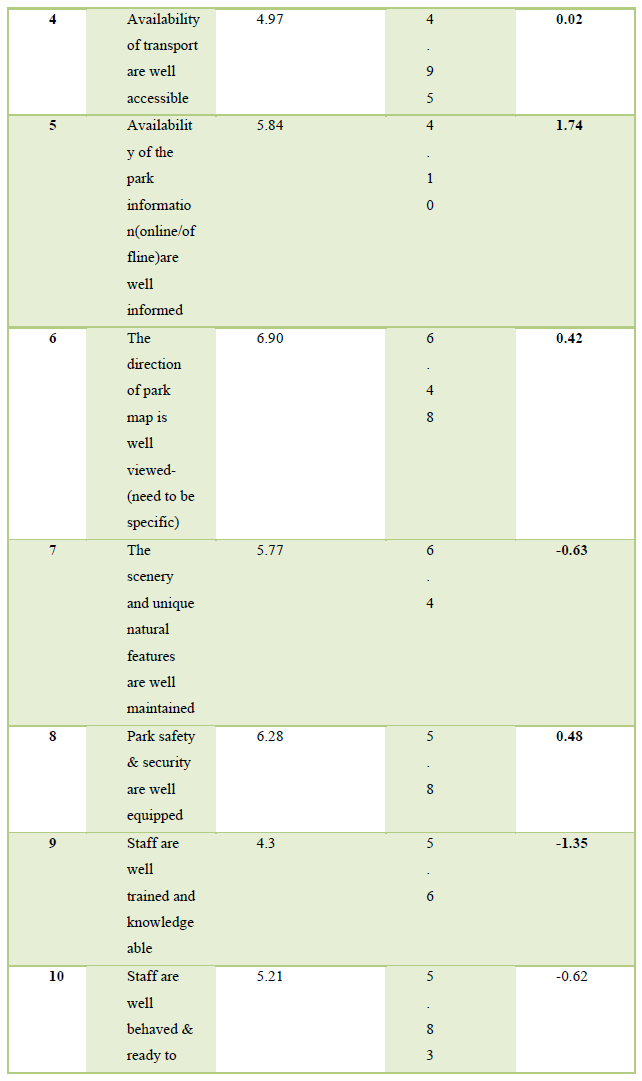
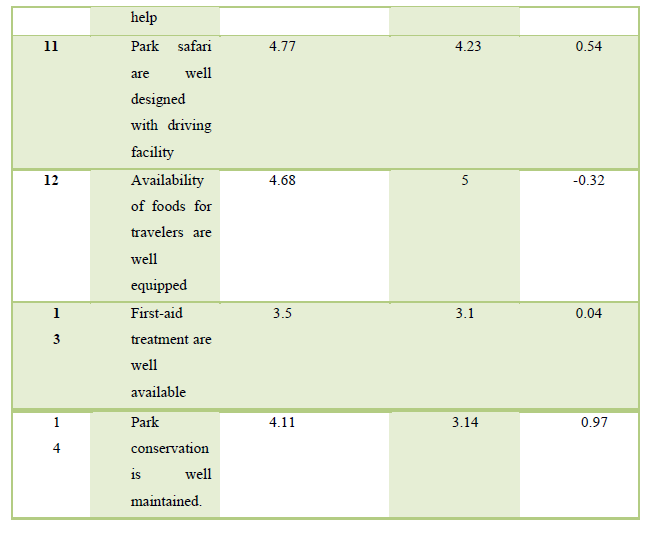



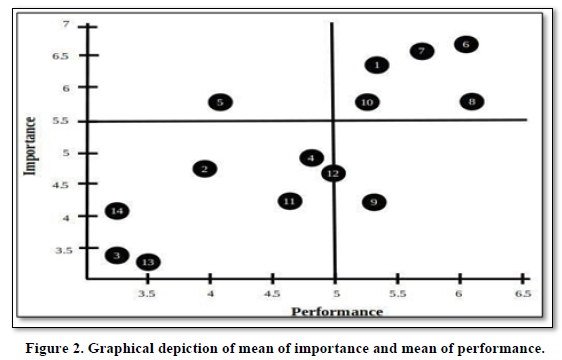
From Figure 2, as we can see the management of Jaldapara national park must be aware and take extra care on several variables. Some of the variables like ‘staff are well trained and knowledgeable’. Availability of the park information (online/offline) are well informed and park safety & security are well equipped, have high importance and low performance. Information about the park in online mode has great importance nowadays for making destination branding and promotion of national parks. Batter safety and security are making tourists feel relaxed. There are 4 factors in quadrant III with low priority and having low essentialness and by and large execution like Location is value for money, Viewpoint location is well area, First-aid treatment is well available, Park conservation is well maintained. There are two more cases on variables like availability of foods for travelers are well equipped, and Staff are well trained and knowledgeable are performance is high but with low importance.
CONCLUSIONS, RECOMMENDATIONS & LIMITATIONS
Analysis of the result has an effective managerial implication which can create destination branding to attract tourists from other states. The executives and Government should have the option to oversee guests desires and this national park should concentrate on some different factors which have some elite and low desires factors. In future some of the other attributes can be added like the economic factor of the tourist and tourist motivation can be analyzed. The research can be explored with a comparative analysis with two or more national parks on time. The incessant essentialness of ‘organization quality’ inside the movement business and organization segment can affect traveler return to reason and the organization office wishes to choose test methodologies which help to look an approach to improve the introduction
of the nationwide park. For the long term, retaining in tourist attractions national parks need to focus on several variables on service quality. Management can utilize research output for understanding tourist behavior through important variables of the national park. For creating destination branding management needs to improve the performance level of low importance variables. The social proximity instigated by traveler WOM as yield leads to traveler satisfaction which provoking spot association should be truly considered by the objective publicizing the administrators to appreciate wayfarer directly. An extensive assessment of factors could be unbelievably valuable for DMOs to see sections to separate and feature travel offers. A clearing evaluation of variables will be incredibly loved for DMOs to peer parts to separate and highlight venture offers. The result of this outcome can investigate a few territories of exploration for research researchers who can profoundly examination the impacts of a portion of different factors like voyages thought process, the portion of wallet in the national park the travel industry sector. Accordance with IPA, the estimations which fall inside the quadrant (Q3) have the best needs and the scale inside the ensuing quadrant are arranged after them. Results of the principal assessment ensure the disclosures. For example, Qu and Sit down (2007) used IPA in their look at identifying the characteristics and weaknesses of the passed-on organizations could be incredibly fundamental for chiefs. With simply controlled assets available, they have to confirm that they use what they have as beneficial as reasonable (Lin, 2009). The current exploration transformed into an undertaking to give an all the more away from of the components which have a more essential critical employment in extending the first rate of organization from clients’ factor of view. in any case, it become speculated that seeing that individuals change broadly in phrases in their persona designs and furthermore concerning reality that the best effortlessly of records is the reviews of those individuals on their emotions and attitudes, it might be mutilation to simply remove each client's craving score from his/her acumen after which process the induce cost for each carrier quality Dimension, hereafter.
Geographical limitation with confounding with one point of location for sample survey might be key limitation for these studies. Size of the sample may not be adequate for these studies. The assessment can be taken up for more broad geographical incorporation with a gigantic guide to have a more summarized idea of a national park in the movement business interest. Cutting-edge assessment can be explored from this assessment by joining a couple of significant promoting and travel questions, namely travel personalization, destination brand, destination communication, destination behaviors etc. New co-relation may be incorporated by understanding the relation between attachment of the destination and new advancing perfect models focused on journeying and travel rehearsals.
Abas, S., Ahmed, S., Norazirah, A. & Fazlina, Y. (2013). An evaluation of service quality from visitors’ perspective: The case of Niah National park in Sarawak. International Journal of Business and Society, 14(1): 61-78.
Arabatzis. G. & Grigoroudis, E. (2010). Forest Policy and Economics 12(2010): 163-172.
Birenboim, A., Clave, S.A., Russo, A.P. & Shoval, N. (2013). Temporal activity patterns of theme park visitors. Tourism Geographies.
Burns, A.C. & Bush, R.F. (1995). New Jersey: Prentice Hall Cronin, Marketing Research.
Babić, H.V., Kalajdžić, M.A., Amra, B. & Amina, S. (2019). IPA & SERVPERF quality conceptualization satisfaction and their role in hotel services satisfaction. Tourism and Hospitality Management, 25(1).
Chen, M., Lee, H.T., Chen, S.H. & Huang, T.H. (2011). Tourist behavioral intentions in relation to service quality and customer satisfaction in Kinmen National Park, Taiwan. International Journal of Tourism Research, 13, 416-432.
Chiappa, G.D. (2013). Internet versus travel agencies: The perception of different groups of Italian online buyers. Journal of Vacation Marketing 19, 55-66.
Chu, R.K.S. & Choi, T. (2000). An importance-performance analysis of hotel selection factors in the Hong Kong hotel industry: A comparison of business and leisure travelers. Tourism Management, 21: 363-377.
DeVellis, R.F. (2003). Scale development: Theory and applications. London: Sage Publications.
Enright, J. & Newton, J. (2004). Tourism destination competitiveness: A quantitative approach. Tourism Management 25, 777-788.
Fick, G.R. & Ritchie, J.R.B. (1991). Measuring service quality in the travel and tourism industry. Journal of Travel Research, 30(2), 2-9.
Fleischer, A., Rotem, A. & Banin, T. (1993). New directions in recreation and tourism activities in the rural sector in Isreal: Demand and Supply Factors. Research Report; Development Study Center: Rehovot, Israel.
Fetene, A., Prasse, R. & Yeshitela, K. (2015). Anthropogenic degradation of wildlife habitats and the need for alternative conservation strategies: The case of Nech Sar National Park, Ethiopia.
Hansen, E & Bush, J. (1999). Understanding customer quality requirements: Model and application. Industrial Marketing Management, 28, 81-91.
Hair, J., Black, B., Babin, R., Anderson, R. & Tatham, R. (2006). Multivariate data analysis (6). New York: Prentice Hall.
Hudson, S., Hudson, P., & Miller, G.R. (2004). The measurement of service quality in the tour operating sector: A methodological comparison. Journal of Travel Research, 42, 305-312.
Indian Express (2013) The return of the rhino. Available online at: https://indianexpress.com/article/news-archive/print/the-return-of-the-rhino/
Kamenidou, I., Mamalis, S. & Priporas, C. (2009). Measuring destination image and consumer choice criteria. The case of Mykonos Island. TOURISMOS: An International Multidisciplinary Journal of Tourism 4, 67-79.
Kozinets, R,V. (1998). Initial reflections on consumer research investigations of cyberculture. Advances in Consumer Research, Joseph Alba and Wesley Hutchinson, Provo, UT: Association for Consumer Research,25, pp: 366-371.
Kuo-Chien, C., Mu-Chen C. & Chia-Lin, H. (2012). Identifying critical brand contact elements of a tourist destination: Applications of Kano’s Model and the Importance-satisfaction Model. International Journal of Tourism Research, 14, 205-222.
J.J. & Taylor, S.A. (1994). SERVPERF versus SERQUAL: Reconciling performance-based and perception-minus expectations measurement of service quality. Journal of Marketing, 58, 125-131.
Martilla, J.A., & James, J.C. (1977). Importance-performance analysis. The Journal of Marketing, 77-79.
Malhorta, N. & Birks, D. (2006). Marketing research: An applied approach. Prentice Hall Financial Times, Harlow, UK.
McTavish, D.G.(1997). Scale validity: A computer content analysis approach. Social Science Computer Review 15, 379-393.
Netemeyer, R.G., Bearden, W.O. & Sharma, S. (2003). Scaling procedures: Issues and applications. London: Sage Publications.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithmal, A. & Berry, L.L. (1988). SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. Journal of Retailing, 64, 12-40.
Stevens, BF. (1995). Price value perceptions of travelers. Journal of Travel Research, 31(2), 44-48.
Tak, K.H., Wan, D. & Ho, A. (2006). Tourists satisfaction, recommendation and revisiting Singapore. Tourism Management, 28: 965-975.
Taplin, R,H. (2012). Competitive importance-performance analysis of an Australian wildlife park. Tourism Management, 33, 29-37.
Tsang, NKF., Lee, LYS., Wong, A., & Chong, R. (2012). THEMEQUAL-adapting the SERVQUAL scale to theme park services: A case of Hong Kong Disneyland. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing 29, 416-429.
Vassiliadis, C., Siomkos, G., Vassilikopoulou, A. & Mylonakis, J. (2006). Product design decisions for developing new tourist destinations: The case of Rhodopi mountain. Tourismos 2, 196-212.
Vassiliadis, C., Priporas, C. & Andronikidis, A. (2013). An analysis of visitor behavior uime blocks: A study of ski destinations in Greece. Tourism Management, 34, 61-70.
Wade, D.J. & Eagles, P.F.J. (2003). The use of importance-performance analysis and market segmentation for tourism management in parks and protected areas: An application to Tanzania’s National Park. Journal of Ecotourism, 2, 196-212.
Wagnew, E,T. (2017). Tourist Services Quality Gap Analysis in National Parks of Ethiopia: Evidence from Nech Sar National Park. Journal of Tourism and Hospitality 6: 319.
Yi-Sung, C., Nien-Te, K., Kuo-Chien, C. & Shih-Ming, H. (2019). Integrating the Kano model and IPA to measure quality of museum interpretation service: A comparison of visitors from Taiwan and Mainland China. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 24(6), 483-500.
Zhang, Q. & Chow, I. (2004). Application of importance-performance model in tour guides’ performance: Evidence from mainland Chinese outbound visitors in Hong Kong. Tourism Management 25, 81-91.




